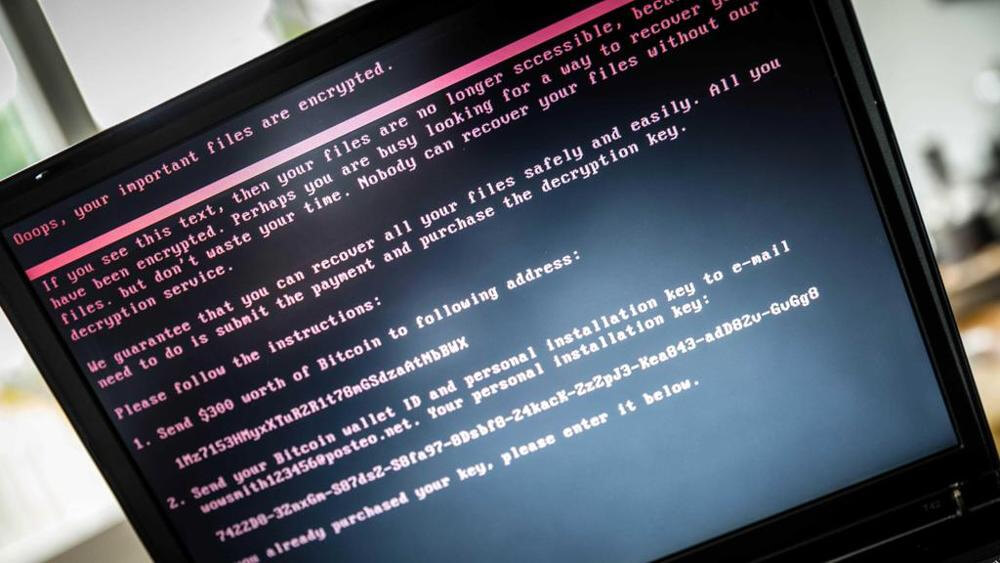
After working its way onto important infrastructure components and encrypting the files of thousands, NotPetya is now considered an intentional cyber attack performed by Russia.
According to White House Press Secretary Sarah Sanders, the Russian military "attack launched in June 2017" and has caused "billions of dollars in damage across Europe, Asia and the Americas." The United States has called the wide sweeping spread of malware indiscriminate and reckless, with promises of consequences incoming.
The official White House statement notes that the end goal of NotPetya was destabilizing Ukraine and infrastructure in other nations. Although NotPetya may appear to masquerade as a relatively sophisticated ransomware, its true purpose was likely never to turn a profit for its creators.
No matter what organization is responsible for a cyber attack, there are some important factors to consider when analyzing how malware spreads. NotPetya relies on the use of a vulnerability in Server Message Block protocol called EternalBlue, which was patched in March 2017. A patch existed to prevent mass spreading several months before NotPetya became a weapon of destruction.
Even though a patch existed to block spreading without user interaction, other methods were still used. Email attachments and websites prompting users to download files still were contributing factors in pushing NotPetya to hundreds of thousands of devices worldwide, including into some Russian businesses.
Due to the nature of cyber attacks, no further details are likely to be released on how links to Russia were found. It is important to stress the need for updates to be installed in a timely manner even if there is no apparent benefit of doing so.